SHAre - An application Specific Instruction Set Processor for SHA-2/3
From iis-projects
Contents
Date
Personnel
Funding
- CTI Project: IISSI
Partners
Summary
In late 2012, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) announced the latest version of the Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA), called SHA-3. Although its predecessor, SHA-2, has neither been broken so far, nor are there any indications that this will take place in the near future, large interest in the SHA-3 competition was shown by both industrial and academic institutions
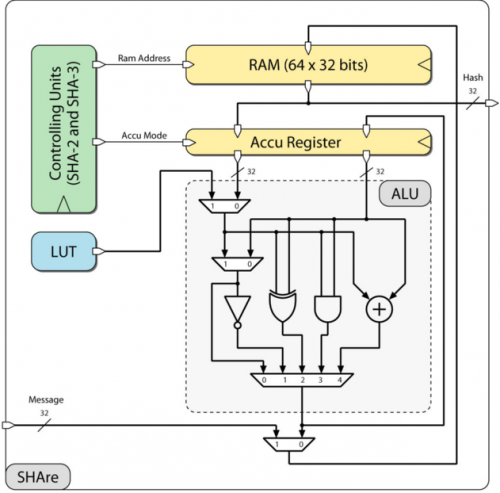
Therefore, this project reduces the 256-bit versions of the two standards to their lowest, reasonable common multiple and aims at a unified, ultra-low area hardware architecture. A 32-bit ALU forms the core component of the design, surrounded by an operand memory and two particular controlling units, one for each hashing algo- rithm. In order to let the design, called SHAre, communicate with its environment, an appropriate interface was accomplished.
The proposed, unified SHAre architecture represents the smallest SHA-2 design published in literature so far and, moreover, offers to calculate a SHA-3 hash as well. This fact should ease the switching from the old standard to the new one, although there is no convincing reason to do so by now from a security point of view. The design re- quires approximately 8.3 kGE targeting a 180 nm CMOS technology by UMC and operates at a maximum frequency of 250 MHz. Hashing of a 512-bit message using SHA-2 and a 1088-bit message using SHA-3, requires about 10,000 and 40,000 clock cycles, respectively.