Difference between revisions of "Design of Scalable Event-driven Neural-Recording Digital Interface"
From iis-projects
(Created page with "==Introduction== Brain Computer Interfaces (BCI) are devices that decode the brain activity and use the decoded information for a wide application range: to control games in t...") |
(→Introduction) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
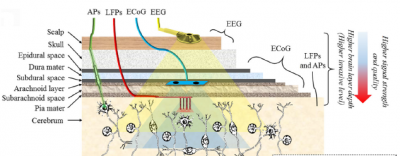
The brain activity can be extracted invasively or not. Invasive methods can be used to sense: the extracellular single neuron activity (action potentials or spikes) with very tiny electrodes close to the neuron; an average communication among neurons close to the electrode via neuron’s axons can also be sensed from local field potentials – LFPs. Finally, ECoG is the signal used to acquire even more neurons ‘activity further from the brain, but still implanted under the skull. | The brain activity can be extracted invasively or not. Invasive methods can be used to sense: the extracellular single neuron activity (action potentials or spikes) with very tiny electrodes close to the neuron; an average communication among neurons close to the electrode via neuron’s axons can also be sensed from local field potentials – LFPs. Finally, ECoG is the signal used to acquire even more neurons ‘activity further from the brain, but still implanted under the skull. | ||
Non-invasive methods are also possible by sensing EEG signals with electrodes very far from the neurons. Such electrodes are placed on the scalp and acquire the macro-scale activity of the brain at very low frequency (< 40Hz). | Non-invasive methods are also possible by sensing EEG signals with electrodes very far from the neurons. Such electrodes are placed on the scalp and acquire the macro-scale activity of the brain at very low frequency (< 40Hz). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Brain_signal_electrodes.png|thumb|400px]] | ||
Revision as of 23:28, 16 July 2018
Introduction
Brain Computer Interfaces (BCI) are devices that decode the brain activity and use the decoded information for a wide application range: to control games in the entertainment field, to predict epileptic seizures or in more to control the seizures, to simply record data for scientific studies. The brain activity can be extracted invasively or not. Invasive methods can be used to sense: the extracellular single neuron activity (action potentials or spikes) with very tiny electrodes close to the neuron; an average communication among neurons close to the electrode via neuron’s axons can also be sensed from local field potentials – LFPs. Finally, ECoG is the signal used to acquire even more neurons ‘activity further from the brain, but still implanted under the skull. Non-invasive methods are also possible by sensing EEG signals with electrodes very far from the neurons. Such electrodes are placed on the scalp and acquire the macro-scale activity of the brain at very low frequency (< 40Hz).