VLSI Implementation of a Low-Complexity Channel Shortener for 2G EC-GSM-IoT and Evolved EDGE
From iis-projects
Introduction
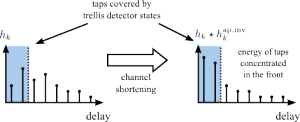
Today's wireless devices have to deal with multi-path propagation caused by reflecting objects along the receive paths. These reflections lead to a long channel impulse responses, which makes the channel equalization complex. Therefore channel shortening filters are used to transform the long channel impulse response into a shorter one as illustrated in the figure. At IIS during the last years, several channel shortening algorithms and implementations have been presented. While dual-diversity streams have been introduced with the Evolved EDGE 2G cellular system [1], the recent EC-GSM-IoT standard achieves up to 20 dB coverage extension by means of up to 64 blind repetitions [2]. The blind repetitions can be seen as multiple diversity streams.
Project Description
Just recently a Mutual Information Lower Bound (MILB) detector was published [3]. It combines multiple diversity streams before equalization, thus requiring a single stream equalizer only. A simplified block diagram of the MILB detector is depicted in Figure 2. It has I/Q samples of N diversity streams as input and outputs Log-Likelihood Ratios (LLR) at its output. The detector consists of channel estimation, variance estimation, shortening filter, and a Max-Log-MAP (MLM) equalizer. The overall goal of this project is the first ASIC realization of a MILB detector with support for the entire 2G GSM based cellular standard family ranging from extended coverage EC-GSM-IoT to high throughput Evolved EDGE. However, the work load would be beyond the scope of a semester project. Therefore, a floating-point, fixed-point, and HDL model of an MLM equalizer will be provided by the supervisors. Furthermore, a Matlab framework will be provided, as well. The students will implement the channel estimation, variance estimation, channel shortener, and glue logic to complement the provided MLM equalizer towards a full MILB detector. Synthesis and place and route of the entire detector conclude the targeted ASIC implementation.
Status: In Progress
- Students: Robert Balas (sem16h28) and Georg Rutishauser (sem16h7)
- Supervision: Benjamin Weber, Matthias Korb
Professor
References
[1] 3GPP. Release 7. http://www.3gpp.org/release-7, 2007.
[2] 3GPP. Release 13. http://www.3gpp.org/release-13, 2016.
[3] Sha Hu, Harald Kröll, Qiuting Huang, and Fredrik Rusek. A Low-complexity Channel Shortening Receiver with Diversity Support for Evolved 2G Devices. In IEEE International Conference on Communications, 2016.