Difference between revisions of "Adaptively Controlled Polarization And Hysteresis Curve Tracing For Polymer Piezoelectrics (1 S/B)"
From iis-projects
(→Links) |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
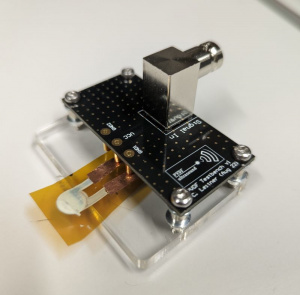
| − | [[Image:PvdfTestbench.jpg|thumb]] | + | [[Image:PvdfTestbench.jpg|thumb| Polymer transducer under test]] |
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Short Description== | ==Short Description== | ||
| − | In the fabrication | + | In the fabrication of '''piezoelectric materials''', a '''polarization step is required''' to create and maintain a permanent electric dipole moment in the crystal structure of the material. The polarization process typically involves applying a constant or alternating high electric field to the piezoelectric material over a period of time. This field creates an electric polarization in the material by reorienting the crystal structure and aligning the electric dipoles in the direction of the electric field. |
| − | To measure the success rate of the polarization process, the polarization of the material is plotted against the applied electric field. The frequency response of the applied signal results in a hysteresis-shaped curve | + | To measure the success rate of the polarization process, the polarization of the material is plotted against the applied electric field. The '''frequency response''' of the applied signal results in a '''hysteresis-shaped curve that is used to evaluate the piezoelectric properties''' of the material. |
| − | Due to the high electric fields and often unknown material parameters, manual control of such | + | Due to the high electric fields and often unknown material parameters, manual control of such devices can be difficult. The '''goal of this work''' is to develop a '''microcontroller-based strategy''' for polarization and testing of piezoelectric polymers. It also aims to design the digital architecture in such a way that later studies will allow '''ML-based control of the system'''. |
| + | |||
| + | ==Relevance== | ||
| + | The development of a digital architecture that enables ML-based control of polarization and testing can revolutionize the state of the art of polarization and measurement equipment in the piezoelectric industry. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 21: | ||
===Prerequisites=== | ===Prerequisites=== | ||
: Analog Mixed Signal Design | : Analog Mixed Signal Design | ||
| + | : High Voltage | ||
: PCB Design | : PCB Design | ||
: Microcontrollers | : Microcontrollers | ||
| Line 48: | Line 52: | ||
==Detailed Task Description== | ==Detailed Task Description== | ||
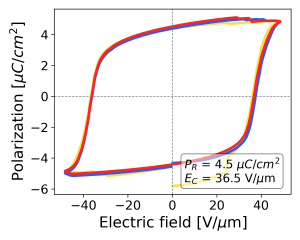
| + | [[Image:PvdfHysteresis.png|thumb| Hysteresis curve of a polymere transducer]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The main objective of this work is to develop a microcontroller-based strategy for polarization and testing of piezoelectric polymers. The digital architecture is to be designed in such a way that ML-based control of the system is possible. | ||
===Goals=== | ===Goals=== | ||
| − | + | * Familiarization with the literature and the analog design of the existing manually controlled system. | |
| + | * Creating a model for microcontroller-based system controls. | ||
| + | * Developing software to run on the microcontroller in order to pilot the polarization process and track hysteresis curves | ||
| + | * Testing of the developed control strategy on transducer samples | ||
| + | * PCB design of the new system architecture | ||
| + | * Testing of the complete system on transducer samples | ||
===Practical Details=== | ===Practical Details=== | ||
| Line 68: | Line 80: | ||
[[Category:Digital]] | [[Category:Digital]] | ||
| + | [[Category:UScharacterization]] | ||
[[Category:FlexEmbedded]] | [[Category:FlexEmbedded]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Ultrasound]] | ||
[[Category:Available]] | [[Category:Available]] | ||
[[Category:Group Work]] | [[Category:Group Work]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:14, 21 July 2023
Contents
Short Description
In the fabrication of piezoelectric materials, a polarization step is required to create and maintain a permanent electric dipole moment in the crystal structure of the material. The polarization process typically involves applying a constant or alternating high electric field to the piezoelectric material over a period of time. This field creates an electric polarization in the material by reorienting the crystal structure and aligning the electric dipoles in the direction of the electric field.
To measure the success rate of the polarization process, the polarization of the material is plotted against the applied electric field. The frequency response of the applied signal results in a hysteresis-shaped curve that is used to evaluate the piezoelectric properties of the material.
Due to the high electric fields and often unknown material parameters, manual control of such devices can be difficult. The goal of this work is to develop a microcontroller-based strategy for polarization and testing of piezoelectric polymers. It also aims to design the digital architecture in such a way that later studies will allow ML-based control of the system.
Relevance
The development of a digital architecture that enables ML-based control of polarization and testing can revolutionize the state of the art of polarization and measurement equipment in the piezoelectric industry.
Status: Available
- Looking for 1 Semester/Bachelor students
- Contact: Christoph Leitner
Prerequisites
- Analog Mixed Signal Design
- High Voltage
- PCB Design
- Microcontrollers
Character
- 20% Literature research
- 40% PCB Design
- 30% Microcontroller programming
- 10% Testing
Professor
Detailed Task Description
The main objective of this work is to develop a microcontroller-based strategy for polarization and testing of piezoelectric polymers. The digital architecture is to be designed in such a way that ML-based control of the system is possible.
Goals
- Familiarization with the literature and the analog design of the existing manually controlled system.
- Creating a model for microcontroller-based system controls.
- Developing software to run on the microcontroller in order to pilot the polarization process and track hysteresis curves
- Testing of the developed control strategy on transducer samples
- PCB design of the new system architecture
- Testing of the complete system on transducer samples
Practical Details